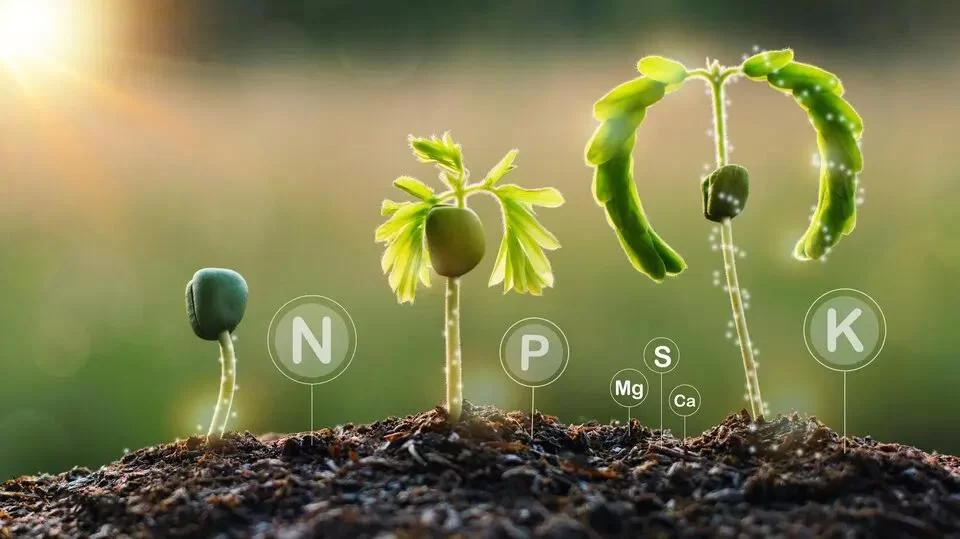
Understanding the Importance of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium in Plant Growth
As a gardener, I’ve often found myself looking at the rows of plants in my garden and wondering how I can help them grow healthier, produce better flowers, and bear more fruit. Over the years, I’ve come to understand that a balanced nutrient supply is crucial for plant health, and three nutrients stand out in this regard: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (often referred to as NPK). Each plays a vital role in plant growth, and understanding their ratios can help us make better decisions when choosing fertilizers and soil amendments.
1. What Are Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium?
First, let’s break down what nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium actually are and why they are so essential for plant health. These three elements, often labeled as the NPK nutrients, are the building blocks that plants need to grow strong and vibrant.
Nitrogen (N) is vital for plants because it is a primary component of chlorophyll, the green pigment in leaves. It helps plants produce energy through photosynthesis, which is essential for healthy growth. Without enough nitrogen, plants will have yellowing leaves and poor growth.
Phosphorus (P) supports strong root development and helps plants form flowers and fruits. It also plays a critical role in energy transfer within the plant. When plants don’t get enough phosphorus, they may exhibit slow growth, weak stems, and poor flowering.
Potassium (K) helps plants develop strong stems and roots, and it enhances their ability to resist disease, drought, and extreme temperatures. Potassium is often considered the “immune booster” of plant nutrients, promoting overall plant vigor.
2. The Role of NPK Ratios in Fertilizers
When you buy fertilizer, you’ll often see numbers like “10-10-10” or “5-10-10” printed on the package. These numbers represent the ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in the fertilizer. The ratio of these nutrients is important because it directly affects how plants grow.
For example, a fertilizer with a higher nitrogen ratio (e.g., 30-10-10) is ideal for plants that need strong leafy growth, like lettuce or spinach. On the other hand, a fertilizer with more phosphorus (e.g., 10-20-10) is better for plants that need strong root systems, such as tomatoes or roses. Finally, a fertilizer with more potassium (e.g., 10-10-20) is great for helping plants resist disease and environmental stress.
3. How to Choose the Right NPK Ratio for Your Garden
Choosing the right NPK ratio depends largely on the type of plants you are growing and the specific needs of your soil. Here’s a simple guide:
- For leafy vegetables like lettuce, spinach, and kale, look for fertilizers with a higher nitrogen content (e.g., 20-10-10 or 24-8-16).
- For fruiting plants like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, opt for a balanced ratio (e.g., 10-10-10 or 5-10-5), or one with a bit more phosphorus to support flower and fruit development.
- For flowers and ornamental plants, a higher phosphorus ratio (e.g., 10-20-10) will encourage blooming and root development.
- For lawns, a balanced NPK ratio (e.g., 16-4-8) will help maintain healthy growth while promoting strong roots.
4. How to Test Your Soil's Nutrient Levels
Before adding any fertilizer, it’s a good idea to test your soil to determine what nutrients it may be lacking. Many local garden centers offer soil testing kits, or you can send a sample to a professional laboratory. Knowing the nutrient levels in your soil will help you avoid over-fertilizing, which can harm your plants and the environment.
For example, if your soil test reveals that your soil is low in nitrogen, you can choose a fertilizer with a higher nitrogen content. If your soil is already rich in potassium, you may not need to add any more potassium-based fertilizers.
5. The Consequences of Incorrect NPK Ratios
Over- or under-fertilizing your plants can lead to a variety of problems. Too much nitrogen, for instance, can cause excessive leafy growth at the expense of flowers and fruit. On the other hand, a lack of nitrogen can result in yellowing leaves and stunted growth. Similarly, too much potassium can interfere with the plant’s ability to absorb other nutrients, leading to nutrient imbalances.
In my own garden, I once made the mistake of using a high-nitrogen fertilizer on my tomato plants, thinking it would help them grow faster. However, the result was an overabundance of leaves but very few fruits. It took me some time to realize that what I needed was a fertilizer with more phosphorus to support flowering and fruiting. This experience taught me the importance of understanding nutrient ratios and using fertilizers thoughtfully.
6. Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Fertilizing
When it comes to gardening, balance is key. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium each play a distinct role in plant health, and understanding how to use them in the correct proportions can make all the difference. Whether you're growing vegetables, flowers, or just maintaining a healthy lawn, keeping an eye on your soil’s nutrient levels and selecting the right fertilizers will help ensure that your plants grow strong, healthy, and productive.
By understanding the science behind NPK ratios, I’ve been able to nurture my garden in a way that supports both healthy growth and long-term sustainability. And I’m confident that with the right knowledge, you can do the same in your own garden, too!